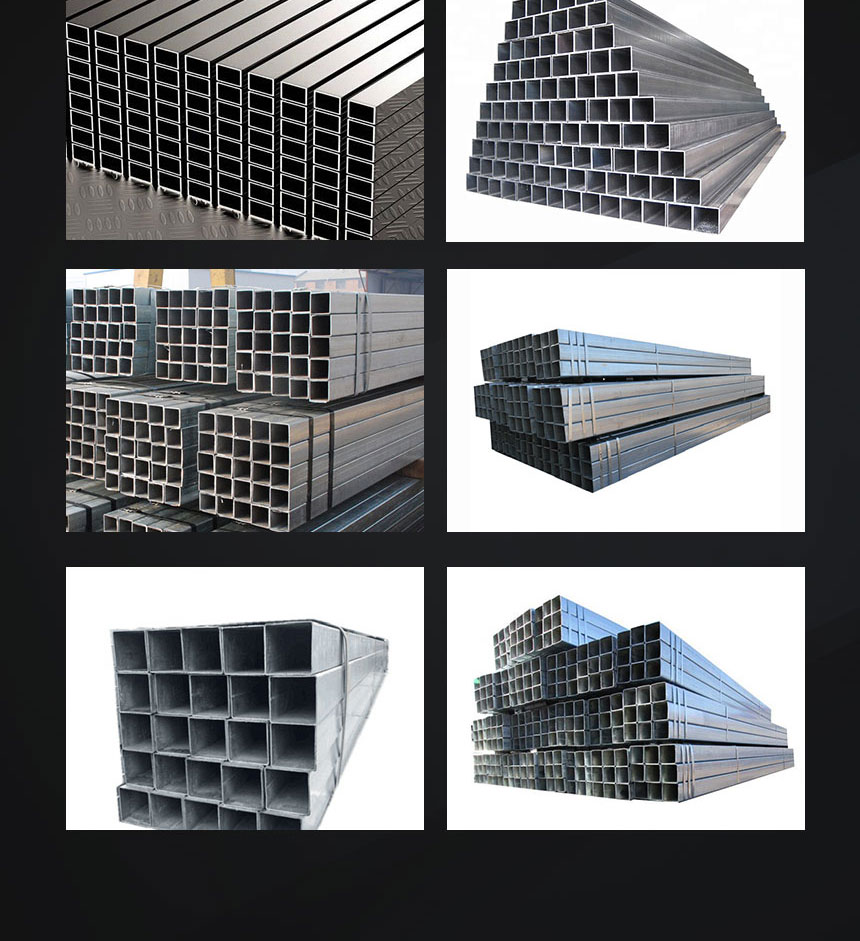
Product Introduction
Hot dip galvanized pipe
The hot-dip galvanized pipe is to make the molten metal react with the iron matrix to produce an alloy layer, so that the matrix and the coating are combined. Hot-dip galvanizing is to pickle the steel pipe first. In order to remove the iron oxide on the surface of the steel pipe, after the pickling, it is cleaned in a tank of ammonium chloride or zinc chloride aqueous solution or a mixed aqueous solution of ammonium chloride and zinc chloride, and then sent to Hot dip plating tank. Hot-dip galvanizing has the advantages of uniform coating, strong adhesion and long service life. The matrix of the hot-dip galvanized steel pipe undergoes complex physical and chemical reactions with the molten plating solution to form a corrosion-resistant zinc-iron alloy layer with a compact structure. The alloy layer is integrated with the pure zinc layer and the steel pipe matrix, so it has strong corrosion resistance.
Cold galvanized pipe
Cold galvanized pipe is electro-galvanized, and the amount of galvanization is very small, only 10-50g/m2, and its corrosion resistance is much worse than that of hot-dip galvanized pipe. Most of the regular galvanized pipe manufacturers do not use electro-galvanization (cold plating) in order to ensure quality. Only those small enterprises with small scale and outdated equipment use electro-galvanization, and of course their prices are relatively cheaper. The Ministry of Construction has officially announced that cold galvanized pipes with outdated technology should be eliminated, and cold galvanized pipes are not allowed to be used as water and gas pipes. The galvanized layer of cold galvanized steel pipe is an electroplated layer, and the zinc layer is separated from the steel pipe matrix. The zinc layer is thin, and the zinc layer simply adheres to the steel pipe substrate and easily falls off. Therefore, its corrosion resistance is poor. In newly-built houses, it is prohibited to use cold-galvanized steel pipes as water supply pipes.
Hot-dip galvanized steel pipes are widely used in construction, machinery, coal mines, chemicals, electric power, railway vehicles, automobile industry, highways, bridges, containers, sports facilities, agricultural machinery, petroleum machinery, prospecting machinery and other manufacturing industries.
Galvanized steel pipes are welded steel pipes with hot-dip galvanized or electro-galvanized layers on the surface. Galvanizing can increase the corrosion resistance of the steel pipe and prolong the service life. Galvanized pipes have a wide range of uses. In addition to line pipes for conveying water, gas, oil and other general low-pressure fluids, they are also used as oil well pipes and oil pipes in the petroleum industry, especially offshore oilfields, as well as oil heaters and condensate for chemical coking equipment. Pipes for coolers, coal-distilled wash oil exchangers, pipe piles for trestle bridges, and pipes for support frames in mine tunnels
Technica Parameter






Related news
- What is GALVALUME?
- In September, my country exported 3.828 million tons of steel and imported 2.885 million tons
- Production limit scheme introduced spot strong, good or has been partially realized should not catch up
- In the first three quarters, China's steel industry ran smoothly
- Treatment process of galvanized steel pipe
- What is the function of galvanized steel pipe?
- What is galvanized steel pipe?
- What is the difference between inner and outer hot-dip galvanized steel pipe and ordinary galvanized steel pipe
- Is the galvanized steel pipe a hot-dip galvanized steel pipe or a cold-galvanized steel pipe?
- What is the function of galvanized steel pipe?